Child Nutrition Programs aim to provide nutritious meals and snacks for all participants regardless of background. Federal regulations require all Sponsoring Organizations to offer meals and snacks that meet meal pattern requirements while also providing an equal opportunity for participants with disabilities to take part in this benefit. Sponsoring Organizations are required to provide reasonable modifications for participants with medical requests while non-medical requests can be made at the discretion of the Sponsoring Organization’s policy.
Child Nutrition Programs: Include the National School Lunch Program (NSLP), School Breakfast Program (SBP), After School Snacks, Seamless Summer Option (SSO), Fresh Fruit & Vegetable Program (FFVP), Special Milk Program (SMP), Child and Adult Care Food Program (CACFP), Summer Food Service Program (SFSP), and USDA Foods
Sponsoring Organizations: Refers to an organization (school district, child care center, Head Start center, non-profit organization, adult day care, homeless/emergency shelter, Family Day Care Home Provider) taking part in one of the Child Nutrition Programs listed above.
Memos and Guidelines
Federal Guidance
-
USDA Memo SP 59-2016: Policy Memorandum on Modifications to Accommodate Disabilities in the School Meal Program
-
USDA Memo SP 26-2017: Accommodating Disabilities in the School Meal Programs: Guidance and Questions and Answers
Oregon Guidance
- Meeting Meal Accommodations Requirements Video: 39 minute video overview of USDA meal accommodation requirements and Oregon-specific documentation requirements, including use of the Medical Statement, Meal Preference Request Forms, and additional resources available.
Nutritionally Equivalent Milk Substitutes
Nutritionally Equivalent Milk Substitutions
Milk Substitutions At a Glance (SNP sponsors only)
Fluid milk is a required component of most meals within the Child Nutrition Programs. In the CACFP, NSLP, and SBP, Sponsoring Organizations may choose to make nutritionally equivalent milk substitutions available for non-disabled participants who cannot consume fluid milk 7 CFR 210.10(d)(2), 7 CFR 226.20(g)(3)(ii)
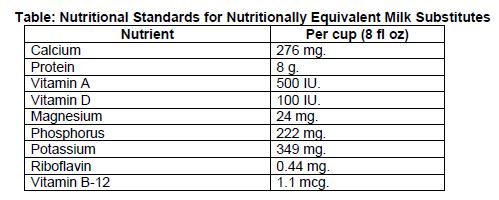
A nutritionally equivalent milk substitute must meet the nutritional standards for fortification of calcium, protein, vitamin A, vitamin D, and other nutrients to levels found in cow’s milk, as outlined in the NSLP regulations at
7 CFR 210.10(d)(2) and shown below.
Sponsoring Organizations may use the ODE Child Nutrition Programs (ODE CNP) developed list of approved nutritionally equivalent milk substitutes shown below. All milk substitutes listed meet the nutritional standards for nutritionally equivalent milk substitutes.
ODE CNP Approved Nutritionally Equivalent Milk Substitutes*:
- Kikkoman Pearl Organic Soymilk Smart Chocolate 8 oz
- Kikkoman Pearl Organic Soymilk Smart Creamy Vanilla 8 oz
- Kikkoman Pearl Organic Soymilk Smart Original 8 oz
- Kikkoman Pearl Organic Soymilk Smart Unsweetened 8 oz
- Pacific Foods Utra Soy Original
- Silk Very Vanilla Soymilk 8 oz
- Silk Chocolate Soymilk 8 oz
- Silk Original Soymilk
- West Life Organic Vanilla Soymilk with Calcium and Vitamin D
- West Life Organic Plain Soymilk with Calcium and Vitamin D
*Notes:The specific products and flavors listed above will meet the nutritional standards to be nutritionally equivalent to cow's milk. Manufacturers may have several different products with similar packaging and product names but different nutritional make-up. Any products that do not match the items listed above will require additional documentation from the manufacturers.
Sponsoring Organizations serving children ages 5 and younger on the CACFP meal pattern can only use plain/unflavored milk substitutes as part of a reimbursable meal.
This list is not all-inclusive of all beverages that may be available in the retail or commercial grocery marketplace. ODE CNP provides the list of nutritionally equivalent milk substitutes based on information received from Sponsors and/or manufacturers and is not an endorsement of the product.
If the fluid milk substitute requested is not one of the ODE CNP Approved Nutritionally Equivalent Milk Substitutes, the exercise and worksheet below should be used to identify if the fluid milk substitute meet the standards shown in the chart above.
Sponsoring Organizations who choose to serve a nutritionally equivalent milk substitute to a participant must collect and maintain the following documentation to receive reimbursements for meals served under Child Nutrition Programs:
- A written request from the parent/guardian, adult participant, or licensed state health care provide. The ODE CNP Meal Preference Request Form can be used for this purpose.
- Menu Documentation showing the nutritionally equivalent milk substitute was served as part of a reimbursable meal.
- Supporting documentation showing the milk substitute served meets nutritional equivalency.
- If the item is an ODE CNP Approved Nutritionally Equivalent Milk Substitute – save packaging information and receipts verifying the purchase.
- If the item is NOT an ODE CNP Approved Nutritionally Equivalent Milk Substitute – save packaging information, receipts verifying purchase, manufacturer’s nutrition label or product formulation statement, and completed Worksheet on Determining Whether a Fluid Milk Substitute Meets USDA Nutrient Requirements.
Forms
Medical Statement to Request Special Meals and/or Accommodations
This form supports special meals or meal accommodations due to medical need. Forms must be signed by a State Licensed Health Care Professional.
Meal Preference Request Form
This form supports non-medical meal accommodations. All accommodations must be consistent with all Child Nutrition Program requirements in order to be reimbursed.

Additional Resources
ODE CNP Handouts and Resources
- Meal Accommodation Decision Tree: This handout provides a visual guide on whether meal accommodation requests can be accommodated and the forms that will be needed.
- Requesting Meal Accommodations: A handout for Section 504/ADA Coordinators and families seeking information on requesting meal accommodations or modifications in the Child Nutrition Programs.
External Resources
-
FARE Back to School Headquarters: This page from the Food Allergy Research & Education (FARE) group provides information on managing food allergies in the classroom and cafeteria. The toolkit provided is targeted to educators and families.